Although China was always perceived as a tea market, coffee is becoming very trendy among young consumers in the country. Coffee drinking culture copied from the Western lifestyle results in Shanghai being the most cafe-crowded city. In 2021 the city beat Tokyo and London, placing itself in the first position for the biggest amount of coffee shops with 6,913 locations and the numbers are still growing.
According to the analysis of the coffee market reported by Chinabgao, the growth rate of coffee consumption in China is about 20% per year, more than 2% above the global growth rate. Experts believe that the Chinese coffee market could reach trillions of yuan within 10 years. In this blog post, we will examine the coffee market in China and talk about opportunities for foreign manufacturers and exporters of coffee beans and coffee brands in the Chinese coffee industry.
Need a cost effective TP (Tmall Partner) to sell in China?
We are an Official Tmall Partner e-commerce Agency. Our Services: E-Commerce, Search Engine Optimization, Advertising, Weibo, WeChat, WeChat Store & PR.
Chinese Coffee Market in 2022
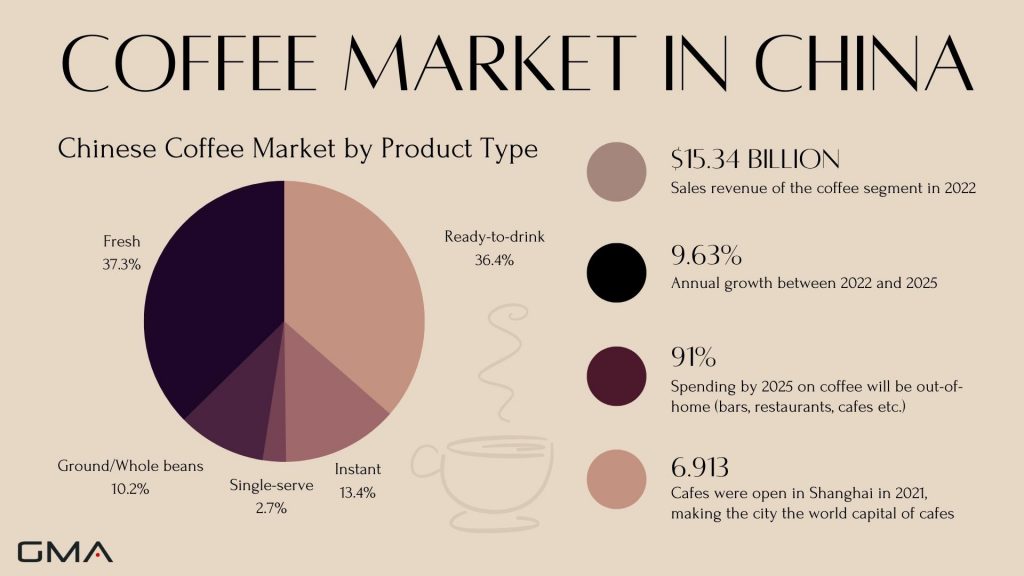
According to Statista, the revenue of the coffee segment in China amounts to 15.34 billion dollars in 2022 and it is expected that the market will grow annually by 9.63% between 2022 and 2025. By 2025, 91% of spending and 34% of volume consumption in the Coffee segment will be attributable to out-of-home consumption (e.g., in bars and restaurants).
The rise of the Chinese middle class and a better standard of living has allowed the opening of hundreds of new coffee shops throughout China. According to Mordor Intelligence, the coffee market was the least affected industry during the COVID-19 pandemic. What is interesting is that in 2020, when all of the countries in the world were struggling with the virus, in Chengdu every day one new cafe was being opened, reaching a total number of 4000, putting Chengdu in third place right after Shanghai and Beijing.
Although per capita consumption in China was only around nine cups in 2021, experts agree that China’s coffee market is one of the most promising ones.
Chinese people prefer ready-to-drink (RTD coffee) and instant coffee formats, which explains the huge success of Starbucks, Costa Coffee, and other coffee franchises in the Chinese coffee market. Instant coffee is also a growing segment of the coffee market and most of the instant coffee drunk in China is imported from giants like Nestle, G7, or Lim’s.
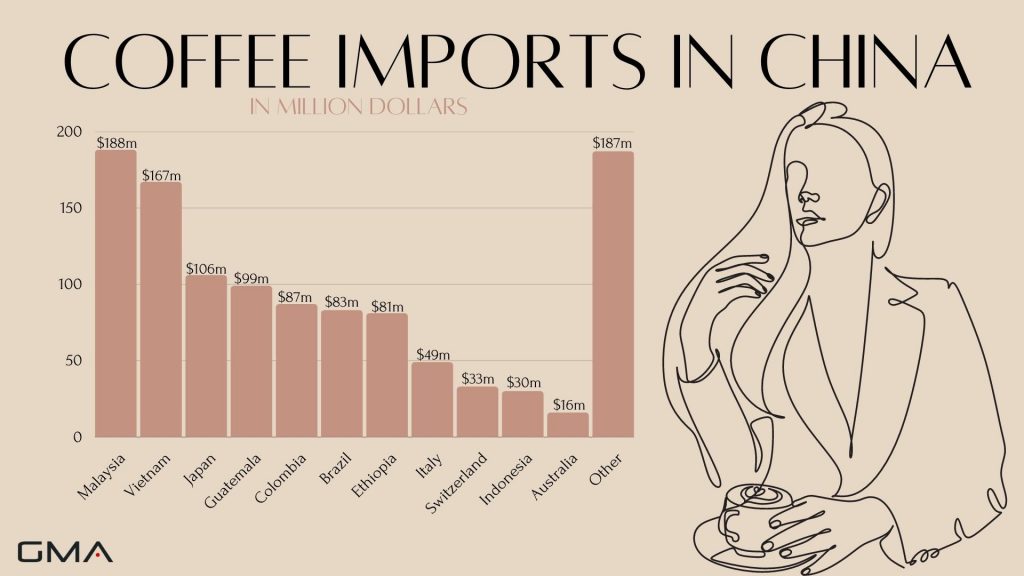
Most of the coffee in China is imported
China is known worldwide for producing its traditional drink – tea and the provinces that produce the most of it are Yunnan and Hainan, two southern provinces of China. What is interesting is that after the introduction of coffee in China in the XIX century, the province started producing coffee beans as well, resulting in the production of 99% of Chinese coffee as of today.
According to Daxue Consulting, despite home production, most of the coffee consumed in China is imported and the coffee from Yunnan is actually exported to Germany, Japan, and US. Most of the coffee in China is imported from Malaysia and Vietnam but there are also many other countries on the list;
Chinese Millennials are the leaders in coffee consumption
Chinese Millennials, born in the 80s and 90s and now between 20 and 39 years old, are hitting prime consumption age. Described as educated, open-minded, and tech-savvy, they make up 31% of China’s total population, representing 415 million consumers.
Chinese Millennials highly cherish individuality and originality and never hesitate to spend more to get the products and services they want. They are health, wellness, and fitness conscious, brand sophisticated. Chinese Millennials are the most profitable coffee drinkers in China, as this is the generation that makes coffee drinking culture more and more known in China.

Tech-savvy Generation
They are far more advanced at e-commerce participation and at integrating tech into everyday life than their Western counterparts. Exploring, purchasing, and interacting online are their daily routines. Therefore, it is no surprise that they are savvy online, active social media users, and relentless mobile shoppers.
According to m.sohu.com, the younger generations of the emerging middle class represent the driving force (75%) of the coffee products boom in the Chinese market. Within this segment, female customers represent the largest share: 70%. They love to meet friends at coffee shops and cafes, and they are used to drinking coffee every morning, or during lunch breaks thanks to them China might become the largest coffee market in the world in the next decades.
You can’t skip quality in China
Young Chinese consumers are demanding and paying particular attention to professionalism, drinks, and services tailored to their tastes, to a style of ceremonial service, to the care of the environment, and the diversification of menus among the various coffees.
Various market players operating above all offline are fighting against competitors active in e-commerce and offering high-quality coffee and food as a weapon to attract customers and offer them good reasons for staying in the long and fruitful coffee in terms of consumption.
Quality is the main determinant of Chinese consumers nowadays and they are willing to pay more for good-quality coffee brands. They spend between 16 to 35 yuan on average for a cup of high-quality coffee.
Major Western brands on the market in China
The coffee culture in China has been on the rise for years thanks to iconic brands like Starbucks and Nestle. The current leaders of this market, with their commitment towards quality but also affordability (many offer discounts during prime days), continue playing an important role as they lead consumers into becoming more aware of what ‘coffee’ truly means, driving the coffee consumption growth to an annual rate of 15% in Mainland China.

Making a ranking of the most competitive brands, in the urban cities, where the western lifestyle is more widespread, Starbucks and Costa firmly hold the top positions in terms of customer flow, according to the statistics of BMI Research in London.
Starbucks is a definite leader in the market, the company actually had a big impact on propagating coffee culture in China and changing consumption habits among Millennials. Nowadays there are more and more instant coffee brands entering the market, but Starbucks still holds its position, thanks to customer loyalty that it gained over more than 20 years in China.
Starbucks in China: Franchise success story
Starbucks’ entry into emerging and developed markets is informed by market research. Starbucks conducted market research to enable a deeper understanding of the Chinese markets, and the way that capitalism functions in the People’s Republic of China (PRC). China contains a number of distinct regionally-based markets, a factor that makes market research crucial to launching new stores and franchises in China.
A deep understanding of intellectual property rights laws is critical to successful market entry in emerging markets. Starbucks articulated an entry strategy that would address the dominant Chinese markets and that was designed to be as inoffensive with respect to the Chinese culture as possible.
Starbucks opened its first store in Beijing in 1999. Through all these years, Starbucks climbed to the position of the market leader, with little competition from other companies. In 2022 Starbucks will reach 6000 opened stores in the country. The biggest Starbucks is located in Shanghai and it’s one of the most popular Starbucks worldwide, with younger generations queueing there on daily basis.

China Localization done right
Market research supported the development of Starbucks’ competitive internationalization strategy. The overarching competitive strategy was to create an aspirational brand. In fact, it was reported that in 2017 Starbucks was opening a store every 15 minutes to keep up with the impressive growth in demand for quality coffee among Chinese coffee drinkers.
Costa in China has focused a lot on the analysis of the local market and is willing to change its offer according to the tastes of consumers in the various regions. For this reason, it is not strange to hear customers say that, for example, Beijing’s Costa coffee tastes slightly different from that of Shanghai. In addition, the English chain offers different types of tea, a quiet environment, and loyalty programs with cards or apps.
Local brands are also gaining popularity among young consumers

Despite the predominant position of the big chains, coffee boutiques not affiliated with big brands are very popular: this type of premises offers a more comfortable environment and service.
LISUN
Founded in 1987 in the province of Hainan, Lisun is the first company to introduce instant coffee in China. It became particularly famous for its coconut coffee. The company owns its own coffee plantation on the island of Hainan. Over the years, it has diversified its product range by launching different tastes of coffee, and other types of beverages on the market, and also selling roasted coffee as well as soluble coffee.
HOGOOD
Hogood is a Yunnan-based company founded in 2007. It is one of the largest coffee growers grown in China and one of the best-selling local coffee brands in the country. Hogood produces and sells roasted coffee, available in both grains and ground, and instant coffee.
LUCKIN COFFEE
Lucking Coffe is a relatively new company on the Chinese market, founded in 2017. It operates on a different business model, operating an app where consumers can order instant coffee for delivery on pick up in one of Luckin Coffee shops, which are more like pick-up counters rather than full-size cafes. Unfortunately, Luckin Coffee had financial problems and filed for bankruptcy in 2021. Although today the company is trying to come back, the future of this coffee brand is yet unknown.

How to sell coffee in China?
Foreign companies that have opened successful online stores all have two common characteristics. They have the know-how to export to China and have a deep knowledge of digital technology. We need to do an important job to promote our brand on Chinese eCommerce platforms, with investments in marketing and communication.
There are few steps to follow to be successful on China’s coffee market (but it actually applies to any other market in China).
Branding – the first step to take in China
Branding is one of the main things to consider when entering Chinese coffee market. Chinese consumers don’t want to buy from brands that they don’t know, so you need to build an online and offline presence in China.
China is not like other international markets and it’s important to gain people’s trust through many different channels.
Landing a Chinese website
Having a Chinese landing page with hosting in China is an interesting and innovative solution created for anyone who wants visibility and success in the Chinese market. Thanks to the hosting of the page in China it is guaranteed the objective to be known in the Chinese market and to create business opportunities, such as looking for customers or partners, as well as Chinese importers or wholesalers.
Chinese consumers looking for information about your coffee brand will check Baidu first and look for your Chinese website there. You can be sure that all the coffee brands on China’s coffee market have their own websites, so if you want to build your online presence and work on your branding, having a website will put you in line with local players.
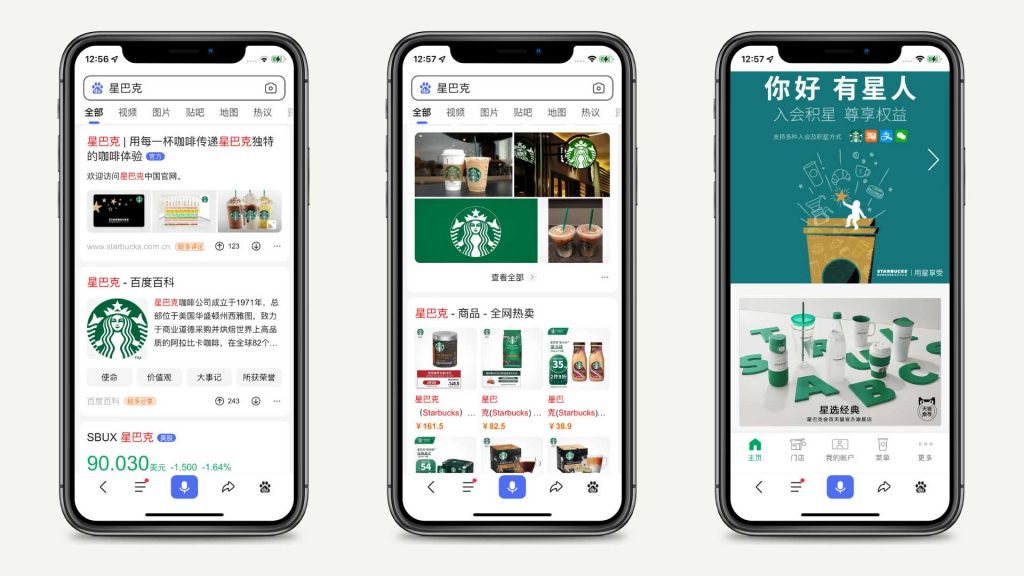
Work on Baidu search engine optimization
A key operation is the optimization of search engines (SEO). The more you sell, the higher the search results appear. Businesses should invest in SEO and buy keywords based on “pay per click”. The higher the price of a keyword, the higher your products will appear in search results. And the more you sell, the more you position yourself at the top. It is essential to participate in online sales events or industry-specific events such as food weeks.
Additionally, having a website in Chinese will help you rank high in Baidu, the biggest search engine in China, because Baidu favours websites in its native language over foreign ones.
Apart from a website, you can also start talking about coffee culture and presenting your brand to Chinese consumers on other Baidu tools, like Baidu Tieba or Baidu Zhidao, which are forums and Q&A platforms. They will help you build good e-reputation on the coffee market in China and you will also get insights from your customers for later improvement.
Here is one of our China’s coffee market case studies:

Social media and storytelling
Social media in China are the main communication tools between brands and customers or potential consumers, as these are the platforms best suitable for online marketing. As most of the coffee consumed in China is by Millennials and Gen Z, if you want to convince those generations to drinking coffee from your brand, you need to do it through social media.
WeChat, Weibo, Little Red Book or Douyin are the platforms that they check for information, recommendations, special offers, reviews of products and many more. They follow their favourite influencers there, they check news, they ask their friend if that coffee that they’ve seen recently is worth trying and many more.

Those platforms also offer a lot of opportunities for brands to promote coffee in China. You can start official accounts, promote through different content formats, like posts, photos, videos, mini-games, live streaming, shops, paid ads and many more. You can sell coffee products directly on the platform, as many of them have their own online marketplaces.
E-commerce platforms and online marketplaces
In China, the B2C model is dominated by the Tmall portal of the Alibaba group. In the second place, there is JD.com. You can also enter other e-commerce platforms, like Taobao, Pinduoduo or Kaola. An increasing number of Chinese people are buying import products online, using some e-commerce platforms authorized by the Chinese government. The marketplace offers obvious advantages:
- Existing and known platform
- Online payments already active
- High traffic
- Assistance 24 / 24-7 / 7
For a marketplace of those mentioned above we are talking about daily visits of millions of users, with an average purchase rate of around 30%, which for some online shops within them also counts in a 50%, once activated optimal customer service and put in place a well-designed promotion and visibility campaign.
E-commerce platforms are the best places to sell products in China, as most of Chinese consumers go there to shop for products they checked online, either on social media platforms or in Baidu. Online marketplaces will give you the biggest visibility on China’s coffee market, but it’s important to know, that to enter them, you need to build your branding and gain good e-reputation first.
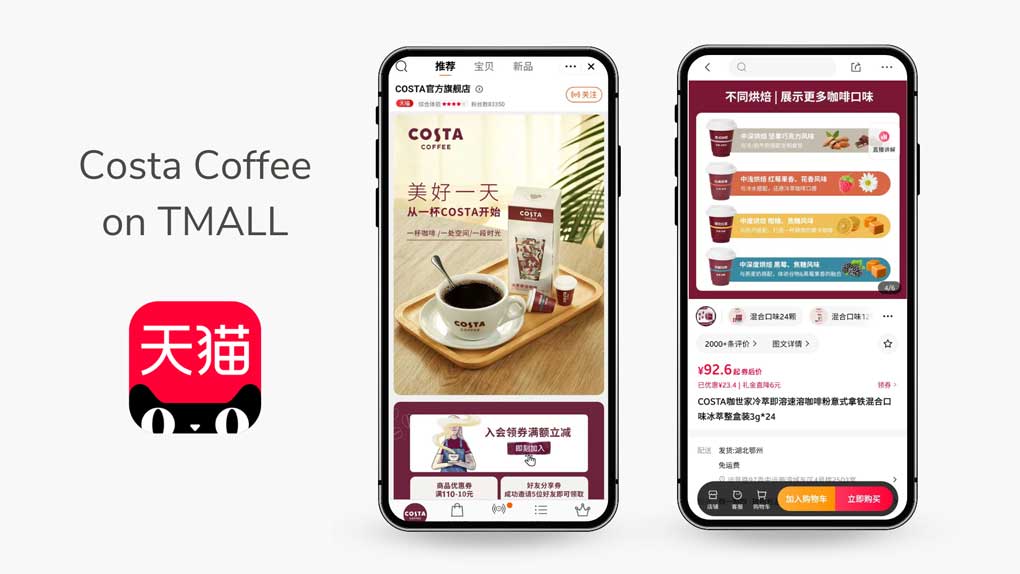
As we mentioned earlier, no one will buy from a brand they never heard off. Entering Chinese e-commerce platforms is expensive, so it’s not worth to do it as a first step, unless you have a distributor that will help you sell coffee on Chinese coffee market.
Find good Chinese coffee distributors for online and offline sales
Any company that wants to grow in China’s coffee market will eventually need to find good distributors, that will help to sell brands’ products on online platforms and in offline stores. They can also help in entering some Chinese coffee shops, cafes and restaurants.
But it’s important to know that finding a distributor is not an easy task and it’s better to trust professionals with trusted contact to find the right Chinese coffee distributors for your brand.
GMA can help you start selling your coffee in China!
Are you thinking to export your coffee brand? Contact GMA digital marketing agency, specializing in the Chinese digital market. We have more than 10 years of experience with working with many different brands from food & beverage industry, but also all the others. We’ve worked with more than 600 brands, helping them on many levels.

We can do a market research and market analysis to check what will work best for your brand. We offer web design services, social media marketing strategies, KOL marketing, store set-up on e-commerce platforms and many more.
Here are some of our case studies from F&B industry:

Don’t hesitate to leave us a comment or contact us to discuss your China coffee business!